A wide array of sensors and modules control your transmission, but what exactly do they do and how do they lead to symptoms of transmission failure?
In many cases, there may be at least ten different modules that directly or indirectly control and provide feedback to your transmission. The number of modules that vehicles use depends on their complexity. Below is a list of various modules and sensors that regulate your automatic transmission. Please note that problems and their causes vary relative to specific makes and models – these are simply the most common. Go to Transmission Repair for more information.
LEARN MORE ABOUT RENO’S TRUSTED TRANSMISSION SHOP
Transmission Control Module (TCM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
All automatic transmissions use a control module to regulate speed, gear changes, and clutch engagement. The TCM makes decisions based on the information it receives from the engine, making it the key to shifting gears and changing the speed. A TCM recognizes when the clutch is engaged and disengaged and reads RPMs, then executes an order based on driver feedback. Some modules have an internal memory that will recall your driving habits and apply that data to your transmission’s performance.
A powertrain control module also controls engine and transmission functions. It is responsible for timing shifts, shift feel, and engaging the clutch. When your PCM fails, your transmission is likely to stop shifting, shift too soft or harsh or cause complete transmission failure.

Bad transmission control module symptoms:
- Improper downshifts while stopping at a traffic light
- Delayed shifting response from lower gears while accelerating
- The transmission automatically to neutral gear without warning
- Inability to shift from neutral gear
- Random shifting between gears
- Slow acceleration
- Getting stuck while driving uphill
Mass Airflow Sensor (MAS)
The Mass Airflow Sensor measures airflow into the engine and uses that information to regulate air and fuel ratios and determine engine load.
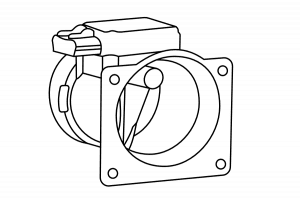
Symptoms of a bad mass airflow sensor:
- Late harsh shifts or early soft shifts
- No shifting
- Decreased engine performance
- Engine labors or hesitates turning over
Throttle Position Sensor (TP)
The Throttle Position Sensor measures throttle (gas pedal) position, having a direct impact on engine performance.
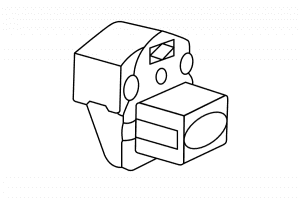
Symptoms of a bad throttle position sensor:
- Late harsh shifts or early soft shifts
- Vehicle bucks or jerks when pressing the throttle
- Sudden stalling
- Hesitation while accelerating
- Check engine light may flash
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAP)
The Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor measures manifold pressure. It’s used to measure engine load. It also measures altitude and controls engine performance.
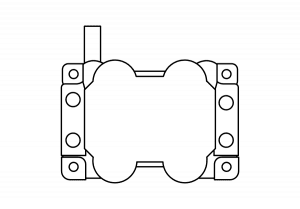
Symptoms of a bad manifold absolute pressure sensor:
- late/harsh shifts, early/soft shifts or no shift at all
- Excessive fuel consumption
- Rough idle
- Hesitation while accelerating
- Sudden stalling
Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IAT)
The Intake Air Temperature Sensor measures the temperature of the air while it enters the intake of the engine. It’s used to control the air/fuel mixture of the engine. It’s also part of the pressure control system for the transmission. As temperature changes, so do the sensor’s electrical resistance and voltage signal.
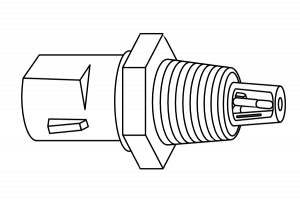
Symptoms of a bad intake air temperature sensor:
- Harder shifting than normal
- Stalling and rough idle
- Slow starts or bursts from the engine
Differential Speed Sensor (DSS)
The Differential Speed Sensor measures vehicle speed. Failure may inhibit activation of overdrive and the converter clutch.
Symptoms of a bad differential speed sensor:
- Poor shifting feel (jerky gear shifting up and down the rev range)
- Cruise control will not activate
- Check engine light
Overdrive Switch (OD)
Overdrive is a function that allows you to cruise at a sustained speed, but reduced engine rpm. This provides better fuel economy, lower noise, and reduced wear on mechanical components. Engaging and disengaging overdrive requires a switch. When this switch fails transmission problems occur.
Symptoms of a bad overdrive switch:
- Transmission won’t shift into overdrive
- The driver is unable to disengage overdrive
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The Vehicle Speed Sensor measures vehicle speed. When it fails the transmission can stop shifting or shift late and harsh. A bad VSS may also inhibit overdrive and the converter clutch.
Symptoms of a bad vehicle speed sensor:
- Check engine light will appear
Air Conditioner Sensor (AC)
The Air Conditioner Sensor signals the PCM when the air condition is on or off. The AC switch will affect engine RPM at a stop. A malfunctioning AC switch can result in problems that feel as though they are transmission related.
Transmission Range Sensor (TR)/ Transmission Position Sensor
The Transmission Range Sensor tells the PCM the position of the transmission shifter. The PCM uses this information to control which gears of the transmission to enable or disable. When the TR sensor fails it can cause wrong gear starts, no upshifts, or what feels like a falling-out-of-gear condition.
Symptoms of a bad transmission range sensor:
- The car doesn’t start and will not move
- Transmission shifts into an unexpected gear
- The vehicle will go into limp mode
Brake Switch
The Brake Switch measures brake pedal position. Its primary function is to release the converter clutch while braking. When it fails the converter clutch won’t apply, or it may chuggle while coming to a stop.
Symptoms of a bad brake switch:
- Brake light stays on while the vehicle is in operation
- Brake lights don’t function
Coolant Temperature Sensor (CT)
The Coolant Temperature Sensor measures engine coolant temperature. It’s used to inhibit overdrive and the converter clutch when the engine is too cold. Failure will severely impact engine performance.
Symptoms of a bad coolant temperature sensor:
- Reduced fuel economy
- Black smoke from the exhaust
- Engine consistently overheating
- Check engine light displays in the dash
Turbine Shaft Sensor (TSS)
The Turbine Shaft Sensor measures input shaft speed. The PCM uses the information provided by the TSS to determine whether or not the transmission is slipping. When it fails it usually results in shift timing problems. Depending on the manufacturer, it can cause multiple shift-timing and shift-feel problems.
Symptoms of a bad turbine shaft sensor:
- Harsh or improper shifting
- Cruise control will not engage
- Check engine light displays in the dash
Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor (TFT)
The Transmission Fluid Temperature sensor measures the temperature of the transmission oil (AFT). Its primary function is to inhibit overdrive and converter clutch operation when cold. On some models, it also inhibits certain gears based on the temperature (too hot or too cold).
Symptoms of a bad transmission fluid temperature sensor:
- Check engine light displays in the dash
- The torque converter will not operate correctly
- Harsh or delayed shifts
- The vehicle goes into limp mode
Connect with General Transmission
If you have any questions regarding a transmission failure, repair or remanufacture, give transmission shops in Reno a call today. General Transmission is a family owned transmission repair shop built on values and integrity and we’re more than happy to answer your questions.
 After Hours Contact
After Hours Contact Finance OPtions
Finance OPtions